What is Malignant Melanoma?
Melanoma is a cancer that begins in the cells of the skin that produce pigmentation (coloration). It is also called malignant melanoma because it spreads to other areas of the body as it grows beneath the surface of the skin. Unlike many other types of cancer, melanoma strikes people of all age groups, even the young.
Melanoma in the Foot
Melanoma that occurs in the foot or ankle often goes unnoticed during its earliest stage, when it would be more easily treated. By the time melanoma of the foot or ankle is diagnosed, it frequently has progressed to an advanced stage, accounting for a higher mortality rate. This makes it extremely important to follow prevention and early detection measures involving the feet as well as other parts of the body.
Causes
Most cases of melanoma are caused by too much exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or tanning beds. This exposure can include intense UV radiation obtained during short periods, or lower amounts of radiation obtained over longer periods.
Anyone can get melanoma, but some factors put a person at greater risk for developing this type of cancer. These include:
- Fair skin; skin that freckles; blond or red hair
- Blistering sunburns before the age of 18
- Numerous moles, especially if they appeared at a young age
What Should You Look For?
Melanoma can occur anywhere on the skin, even in areas of the body not exposed to the sun. Melanoma usually looks like a spot on the skin that is predominantly brown, black, or blue—although in some cases it can be mostly red or even white. However, not all areas of discoloration on the skin are melanoma.
There are four signs—known as the ABCDs of melanoma—to look for when self-inspecting moles and other spots on the body:
 Asymmetry -- Melanoma is usually asymmetric, which means one half is different in shape from the other half.
Asymmetry -- Melanoma is usually asymmetric, which means one half is different in shape from the other half.
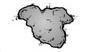 Border -- Border irregularity often indicates melanoma. The border—or edge—is typically ragged, notched, or blurred.
Border -- Border irregularity often indicates melanoma. The border—or edge—is typically ragged, notched, or blurred.
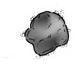 Color -- Melanoma is typically a mix of colors or hues, rather than a single, solid color.
Color -- Melanoma is typically a mix of colors or hues, rather than a single, solid color.
 Diameter -- Melanoma grows in diameter, whereas moles remain small. A spot that is larger than 5 millimeters (the size of a pencil eraser) is cause for concern.
Diameter -- Melanoma grows in diameter, whereas moles remain small. A spot that is larger than 5 millimeters (the size of a pencil eraser) is cause for concern.
If any of these signs are present on the foot, it is important to see a foot and ankle surgeon right away. It is also essential to see a surgeon if there is discoloration of any size underneath a toenail (unless the discoloration was caused by trauma, such as stubbing a toe or having something fall on it).
Diagnosis
To diagnose melanoma, the foot and ankle surgeon will ask the patient a few questions. For example: Is the spot old or new? Have you noticed any changes in size or color? If so, how rapidly has this change occurred?
The surgeon will also examine the spot to determine whether a biopsy is necessary. If a biopsy is performed and it reveals melanoma, the surgeon will discuss a treatment plan.
Prevention and Early Detection
Everyone should practice strategies that can help prevent melanoma—or at least aid in early detection, so that early treatment can be undertaken.
Precautions to avoid getting melanoma of the foot and ankle, as well as general precautions, include:
-
Wear water shoes or shoes and socks—flip flops do not provide protection!
-
Use adequate sunscreen in areas that are unprotected by clothing or shoes. Be sure to apply sunscreen on the soles as well as the tops of feet.
-
Inspect all areas of the feet daily—including the soles, underneath toenails, and between the toes.
-
If you wear nail polish, remove it occasionally so that you can inspect the skin underneath the toenails. Avoid UV radiation during the sun’s peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), beginning at birth. While sun exposure is harmful at any age, it is especially damaging to children and adolescents.
-
Wear sunglasses that block 100% of all UV rays—both UVA and UVB.
-
Wear a wide-brimmed hat.
Remember: Early detection is crucial with malignant melanoma. If you see any of the ABCD signs—or if you have discoloration beneath a toenail that is unrelated to trauma—be sure to visit a foot and ankle surgeon as soon as possible.

